The Triassic Period 248 - 208 Million Years Ago
Homepage > Age of the Dinosaurs - Triassic Period
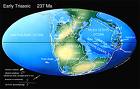
The Triassic Period (about 248 - 208 million years ago) was the first phase of the Mesozoic era (Age of the Middle Life), often called the Age of Dinosaurs. The Earth was a huge super continent called Pangaea ("all Earth"), of which the northern part was called Laurasia and the southern part Gondwana. It had three main environments and was also dominated by prehistoric reptiles suited to dry conditions. Reptiles also took to the air and seas. In the Late Triassic, many of the older reptiles were wiped out, but new kinds took their place. The most successful of these proved to be the dinosaurs.
The Coast Regions
Forests of giant horsetail ferns, tree ferns and ginkgo trees were alive
with insects, amphibians, small reptiles, and early mammals.
The Center of Pangaea
Covered by hot, sandy deserts. Cool areas near the equator had forests
of tall conifers and palm like cycads.
 Triassic
Lands
Triassic
Lands
Laurasia comprised North America, Europe and Asia. Gondwana included Africa,
Arabia, India, Australia, Antarctica, and South America. The south pole
was located over the ocean. Pangaea was slowly drifting north as one big
land mass. This super continent began to show sings of a future breakup
after the Middle Triassic, when cracks appeared in parts of eastern North
America, west and central Europe, and northwest Africa.
Triassic Plants
The type of plants that flourished in Laurasia were those that
were adapted to dry climates, such as ginkgoes, seed ferns, and palm like
cycads and cycadeoids. The biggest trees of this period were conifers.
Ginkgoes formed a fairly open canopy of medium size trees, and cycaids
ranged from short, squat forms to taller, palm like species.
The ferns created the under story un the forests, and low ferns formed savannas in drier open areas that would be grasslands today. Close to the equator and in drier regions, patchy conifer and cycad forests thrived. Tall seed ferns formed forests in Gondwana. Later in the Triassic Period ferns were replaced by cycadeoids and conifers.
 Life
on Land
Life
on Land
Reptiles ruled the land during the Triassic Period. Plant eaters included
dicynodonts, squat, pig like rhynchosaurs, and cynodonts. There were flesh
eating cynodonts as well. Dicynodonts, rhynchosaurs, and most cynodonts
died out in the first of the two mysterious mass extinctions.
The thecodonts that largely took their place died out in the second of those extinctions. Survivors included turtles, land crocodilians,dinosaurs, and small mammals. Both of the main dinosaur groups emerged during the late Triassic.
Among saurischian dinosaurs were bipedal flesh eating theropods and quadruped prosauropods. Early ornithischians were small, bipedal herbivores. With no sea to stop them, dinosaurs quickly colonized the world.
Life in the Air
Small reptiles with wings of skin or scales took gliding flights rom tree
to tree. These wings were supported by long ribs, or they may simply have
been feathery scales growing from arms and legs or webs of skin between
front and hind limbs. Late Triassic animals like these may have given
rise to furry bodied, warm blooded reptiles called pterosaurs. These creatures
had large heads, short bodies, and long skin wings supported by fourth
finger bones. This type of creature was capable of powered flight, unlike
their gliding ancestors.
Life in the Water
Several reptile groups invaded the Triassic seas. Sharp toothed, fish
eating nothosaurus grew up to 13 feet (4 meters) long and had small heads,
long tails and bodies, and paddle like limbs. Seal like placodonts crushed
shellfish between broad, flat back teeth. Ichthyosaurs, up to about 50
feet (15 meters) long, were the reptiles best adapted to the sea. Among
their prey were the big mollusks called ammonoids.
Carnian (228-217 MYA)
The lowermost stage of the Late Triassic System, represented worldwide
by deposited rocks. Named after the Carnic Alps in Europe were it was
first studied by Mojsisovics in 1869. West Gondwanaland (now South America)
is apparently the cradle of the dinosaurs (Eoraptor, Staurikosaurus).